Appearance
多模态RAG实战 - 表格,文本
如需转载,请联系微信群主
许多文档包含混合的内容类型,包括文本和表格。
对于传统的 RAG(检索增强生成),半结构化数据可能具有以下两个主要挑战:
- 文本拆分可能会破坏表格,导致数据在检索中被破坏。
- 将表格嵌入向量化可能会在语义相似性搜索中带来困难。
本实用指南展示了如何在包含半结构化数据(文本 + 表格)的文档上执行 RAG:
我们将使用 Unstructured 来解析文档(PDF)中的文本和表格。 我们将使用 多向量检索器(multi-vector retriever) 来存储原始表格、文本以及更适合检索的表格摘要。 我们将使用 LCEL(LangChain Execution Loop) 来实现所需的链式操作。
整体流程如下:
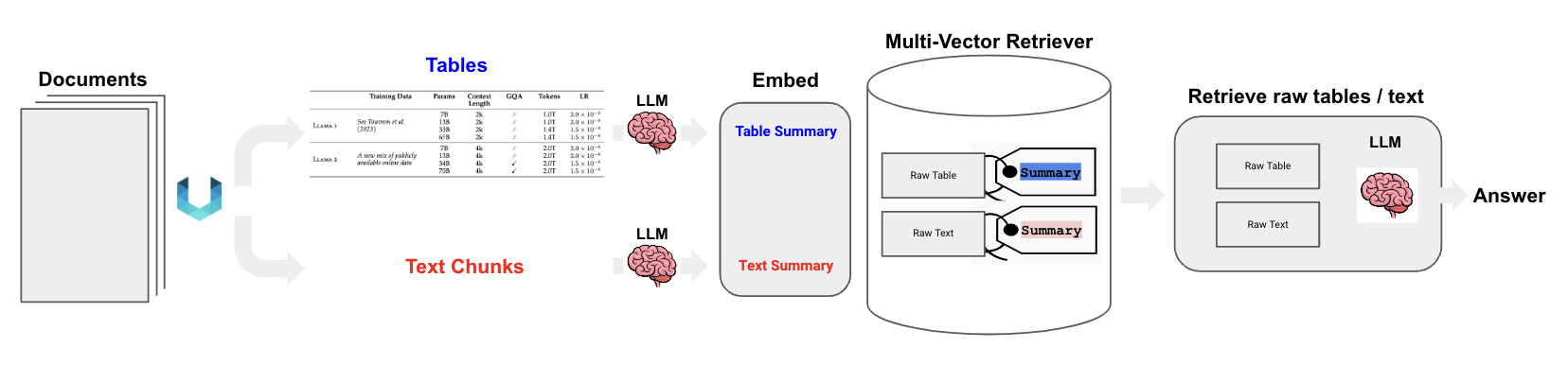
下面我们使用Mac去实现。其他平台如Windows, Linux实现类似。
安装依赖包
在你的Python虚拟环境中安装如下依赖:
pip install langchain langchain-chroma "unstructured[all-docs]" pydantic lxml langchainhub使用Unstructured对PDF进行分区用到如下系统库:
Tesseract:用于光学字符识别 (OCR)。Poppler:用于PDF渲染和处理。
在Mac终端下进行安装:
brew install tesseract
brew install poppler分割PDF中的表格和文本
我们使用:LLaMA2 PDF进行演示。
我们使用Unstructured的partition_pdf方法,它使用布局模型分割PDF文档。
布局模型使得从PDF中提取元素,例如表格成为可能。
我们还可以使用 Unstructured 的 分块处理(chunking):
- 尝试识别文档的各个部分(例如,引言等)。
- 然后,构建保持章节结构的文本块,同时遵循用户定义的分块大小。
path = "/Users/rlm/Desktop/Papers/LLaMA2/"from typing import Any
from pydantic import BaseModel
from unstructured.partition.pdf import partition_pdf
# Get elements
raw_pdf_elements = partition_pdf(
filename=path + "LLaMA2.pdf",
# Unstructured first finds embedded image blocks
extract_images_in_pdf=False,
# Use layout model (YOLOX) to get bounding boxes (for tables) and find titles
# Titles are any sub-section of the document
infer_table_structure=True,
# Post processing to aggregate text once we have the title
chunking_strategy="by_title",
# Chunking params to aggregate text blocks
# Attempt to create a new chunk 3800 chars
# Attempt to keep chunks > 2000 chars
max_characters=4000,
new_after_n_chars=3800,
combine_text_under_n_chars=2000,
image_output_dir_path=path,
)我们可以检查由 partition_pdf 提取的元素。CompositeElement 是聚合的分块。
# Create a dictionary to store counts of each type
category_counts = {}
for element in raw_pdf_elements:
category = str(type(element))
if category in category_counts:
category_counts[category] += 1
else:
category_counts[category] = 1
# Unique_categories will have unique elements
unique_categories = set(category_counts.keys())
category_counts输出:
{"<class 'unstructured.documents.elements.CompositeElement'>": 184,
"<class 'unstructured.documents.elements.Table'>": 47,
"<class 'unstructured.documents.elements.TableChunk'>": 2}class Element(BaseModel):
type: str
text: Any
# Categorize by type
categorized_elements = []
for element in raw_pdf_elements:
if "unstructured.documents.elements.Table" in str(type(element)):
categorized_elements.append(Element(type="table", text=str(element)))
elif "unstructured.documents.elements.CompositeElement" in str(type(element)):
categorized_elements.append(Element(type="text", text=str(element)))
# Tables
table_elements = [e for e in categorized_elements if e.type == "table"]
print(len(table_elements))
# Text
text_elements = [e for e in categorized_elements if e.type == "text"]
print(len(text_elements))输出:
49
184总结文本和表格摘要
使用 多向量检索器multi-vector-retriever 来生成表格的摘要,并可选的生成文本的摘要。
不仅存储摘要,我们还会存储原始的表格元素。
这些摘要用于提高检索的质量,具体内容可以参考多向量检索器文档。
原始表格会传递给大语言模型(LLM),为 LLM 提供完整的表格上下文,以便生成答案。
我这里使用的是GPT-4o-mini对文本和表格进行总结,形成摘要。
首先要配置AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY和AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ""
os.environ["AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"] = ""from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI, AzureOpenAIEmbeddings
prompt_text = """You are an assistant tasked with summarizing tables and text. \
Give a concise summary of the table or text. Table or text chunk: {element} """
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_text)
# 修改这里使用Azure OpenAI
llm = AzureChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
azure_deployment="gpt-4o-mini", # or your deployment
model_version="2024-07-18",
api_version="2024-08-01-preview",
temperature=0,
max_tokens=None,
timeout=None,
max_retries=2,
# other params...
)
summarize_chain = {"element": lambda x: x} | prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# 处理表格元素
tables = [i.text for i in table_elements]
table_summaries.clear() # 清空现有内容
table_summaries.extend(summarize_chain.batch(tables, {"max_concurrency": 5}))
print("表格摘要数量:", len(table_summaries))
print("表格摘要:", table_summaries)
# 处理文本元素
texts = [i.text for i in text_elements]
text_summaries.clear() # 清空现有内容
text_summaries.extend(summarize_chain.batch(texts, {"max_concurrency": 5}))
print("文本摘要数量:", len(text_summaries))
print("文本摘要:", text_summaries)创建检索器
使用多向量检索器:
InMemoryStore存储原始文本和表格。vectorstore存储嵌入文本和表格的摘要。
vectorstore和InMemoryStore使用id进行关联,关联向量化摘要数据和原始数据。
import uuid
from langchain.retrievers.multi_vector import MultiVectorRetriever
from langchain.storage import InMemoryStore
from langchain_chroma import Chroma
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# The vectorstore to use to index the child chunks
vectorstore = Chroma(collection_name="summaries", embedding_function=OpenAIEmbeddings())
# The storage layer for the parent documents
store = InMemoryStore()
id_key = "doc_id"
# The retriever (empty to start)
retriever = MultiVectorRetriever(
vectorstore=vectorstore,
docstore=store,
id_key=id_key,
)
# Add texts
doc_ids = [str(uuid.uuid4()) for _ in texts]
summary_texts = [
Document(page_content=s, metadata={id_key: doc_ids[i]})
for i, s in enumerate(text_summaries)
]
retriever.vectorstore.add_documents(summary_texts)
retriever.docstore.mset(list(zip(doc_ids, texts)))
# Add tables
table_ids = [str(uuid.uuid4()) for _ in tables]
summary_tables = [
Document(page_content=s, metadata={id_key: table_ids[i]})
for i, s in enumerate(table_summaries)
]
retriever.vectorstore.add_documents(summary_tables)
retriever.docstore.mset(list(zip(table_ids, tables)))RAG
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
# Prompt template
template = """Answer the question based only on the following context, which can include text and tables:
{context}
Question: {question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
# LLM
model = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-4")
# RAG pipeline
chain = (
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| model
| StrOutputParser()
)提问:
chain.invoke("What is the number of training tokens for LLaMA2?")结果:
'The number of training tokens for LLaMA2 is 2.0T.'我们可以观察:根据用户问题,召回的是向量化数据库中的下方的表格摘要,如图:
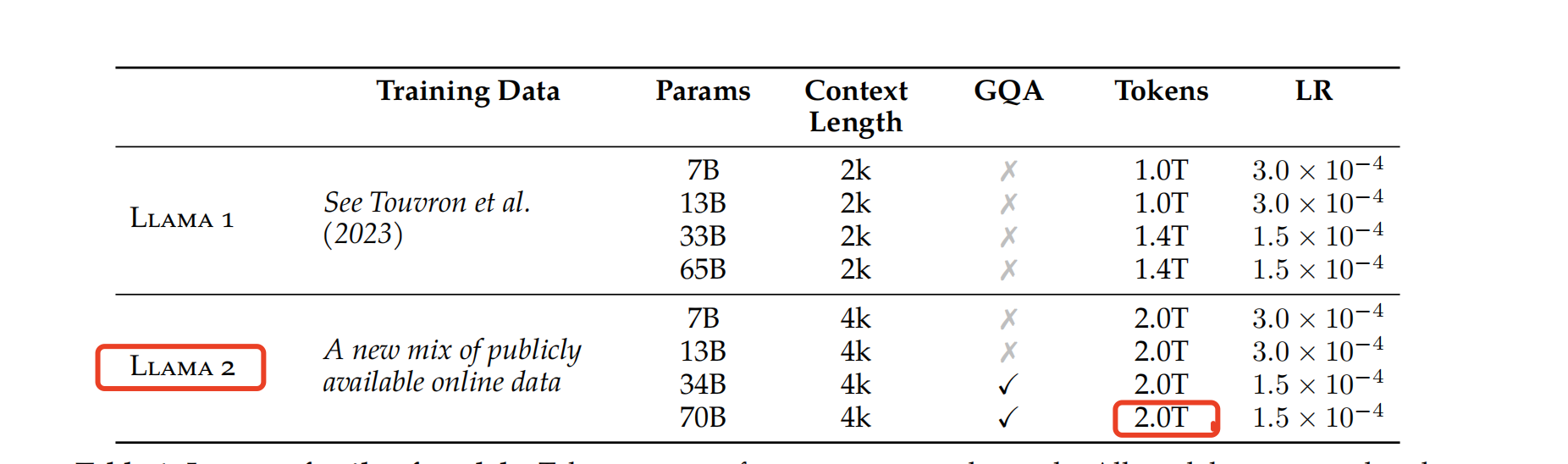
然后将关联的InMemoryStore中存储的原始表格和用户的问题作为LLM的上下文,形成回答。
如需转载,请联系微信群主
加群:
扫描下方二维码加好友,添加申请填写“ai加群”,成功添加后,回复“ai加群”或耐心等待管理员邀请你入群